Reverse Charge Mechanism (RCM) on GST with Journal Entry [2024]
As per Latest RCM Update:
These resolutions will take effect upon notification released on 11 July 2023 by the Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs (CBIC). 50th Meeting of the GST Council had made the following changes.
- 1. Raw cotton provided by farmers to cooperatives, including kala cotton, will now be subject to taxation under the reverse charge mechanism.
- 2. Services rendered by a company’s director to the company in an individual or personal capacity will not be subjected to taxation under RCM.
ac
What is Reverse Charge Mechanism?
In Reverse Charge Mechanism under GST Act 2016, the liability of collecting and depositing GST to government falls on the buyer/ receiver of the goods and services. In certain cases, business entities are required to charge GST under RCM (Reverse Charge Mechanism). You must be wondering why and are you required to reverser charge GST to your vendors.
Under normal GST norms, the supplier of Goods and Services is liable to collect GST from the buyer and then deposit the amount to the government.
This is a comprehensive guide on GST reverse charge, and we will discuss the following.
- 1. How does RCM Work under GST?
- 2. How can We Understand Reverse Charge System with an Example?
- 3. RCM Applicability under GST
- 4. List of Supplies of Services under RCM in GST
- 5. List of Supplies of Goods under RCM in GST
- 6. Why RCM is Necessary?
- 7. Time of Supply under RCM
- 8. RCM Journal Entry with Example
Let’s Get started.
How does RCM Work under GST?
To understand how RCM under GST works, let’s first understand how Goods and Services Tax or any other Indirect Tax work.
Typical working of Goods and Service Tax (GST):
Under GST, businesses are required to charge and collect tax on their sales, and this tax is then remitted to the government. Here is a step-by-step explanation.
- The seller of Goods and Services will add a certain amount of GST to the invoice issued to the buyer.
- The buyer pays the total amount including GST to the seller.
- The seller collects the GST amount received from buyer. (The GST amount collected from the buyer ultimately belongs to the Government.
- The seller then deposits the GST amount after deducting input tax credit (if any) to the government on behalf of the buyer.
Refer to the Infographics below for better understanding.

Working of Reverse Charge Mechanism under GST
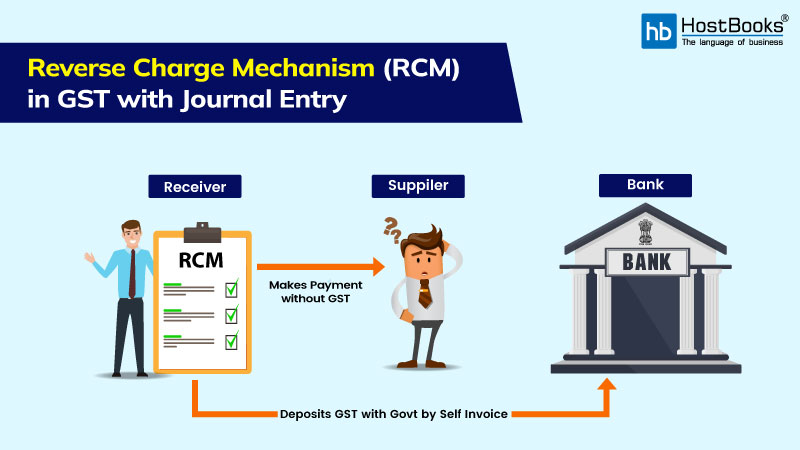
RCM is a concept within the GST system where the liability to pay tax is shifted from the supplier of goods or services to the recipient (buyer) of those goods or services. In simple terms, it means that the buyer becomes responsible for paying the tax directly to the government instead of the seller.
Step By Step Explanation.
- The seller of Goods and Services will issue a non-GST invoice to the buyer. This may be due to exemption or non-registration of GST by buyer.
- The buyer pays the amount excluding GST to the seller according section 31(3)(g) under 9(3) or 9(4).
- The buyer then needs to issue a self-invoice along with the amount of GST payable on it.
- The buyer then deposits the GST amount to the government.
Refer to the Infographics Below.

How can We Understand Reverse Charge System with an Example?
Let’s Understand this with an example of a reverse charge system.
Cashew or (Kaju) falls under the list of goods that fall under reverse charge mechanism. Now let’s suppose a farmer produces cashew worth Rs 30 lakh annually and sells it to a large food processing company that packages it and sells it.
Since the farmer’s turnover is less than GST threshold, he doesn’t need to register in GST. So, the company can technically avoid paying a single penny of GST on purchases if it buys in small quantity from multiple farmers.
Due to this loophole, even after Cashew being a non-essential edible item is exempted from Goods and Service tax.
Therefore, the government introduces Reverse charge mechanism (RCM) under GST rule for Cashews. Now instead of the farmer the company is liable to pay GST on purchasing cashews at applicable rates. It won’t matter if the farmer (seller) is registered or not or the amount.
RCM Applicability under GST
Reverse Charge Mechanism is applicable in 3 major scenarios as per conditions specified by CBIC.
Sections 9(3), 9(4), and 9(5) of CGST and SGST Act deal with reverse charge situations within the state (Intrastate).
On the other hand, for IGST (interstate), the rules are outlined in sections 5(3), 5(4), and 5(5) of the IGST Act.
In Which Cases RCM is Applicable?
CBIC specifies certain goods and services on which GST should be charged on reverse charge mechanism. When a registered dealer purchases these specified goods or services from an unregistered dealer, the recipient (registered dealer) becomes liable to pay the GST directly to the government under RCM.
List of Supplies of Services under RCM in GST as per Section 9(3) of CGST & 5(3) of IGST Act
| S.N. | Service Provider | Service Recipient (Liability to charge GST) |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Provider of goods transportation services | Casual Taxable individuals, corporate bodies, partnership firms, societies, factories, individuals registered under CGST, SGST, IGST Acts |
| 2. | Recovery Agent | Banking Companies, NBFCs, or any financial institutions |
| 3. | Director of a company or a corporate body | Companies or corporate bodies |
| 4. | Individual advocate or advocate firm, Arbitral tribunal | Any business entity |
| 5. | Insurance Agent | Individuals engaged in insurance business |
Here is the detailed list of services chargeable under RCM in GST in 2024.
List of Supplies of Goods under RCM in GST as per Section 9(3) of CGST & 5(3) of IGST Act
| S.N. | Type | Supplier | Recipient |
|---|---|---|---|
| (a). | Cashew nuts, Bidi wrapper leaves, Tendu (Tobacco) Leaves | Agriculturist | Registered person |
| (b). | Silk yarn | Agriculturist | Manufacturer |
| (c). | Supply of lottery | State Govt, Local Authority, UT | Lottery distributor/selling agent |
| (d). | Used vehicles, old and used goods, scrap and waste, seized goods | State Govt, UT, Central Govt, Local Authority | Registered person |
| (e). | Raw cotton | Agriculturist | Registered person |
| (f). | Priority Sector Lending Certificate | Any registered person | Registered person |
Here is the complete list of specified goods subject to RCM as notified by CBIC.
Why Reverse Charge is Necessary?
RCM is primarily implemented to address situations where the government wants to ensure that tax is collected even if the supplier is not registered or is not eligible to pay GST.
This is primarily done to collect taxes even on small deals conducted by businesses with unregistered dealers and sellers.
Unregistered Dealer to a Registered Dealer:
Provision: Section 9(4) of the CGST Act and 5(4) of the IGST Act (Notification No- 07/2019) dated 29 March 2019 applicable w.e.f. 01 April 2019. CGST Tax rate are amended by Notification No- 24/2019 dated 30 September 2019.
This provision ensures that tax is collected even if the supplier is not registered under GST, thereby preventing tax evasion, and promoting compliance.
In this scenario, when a registered buyer purchases goods or services from an unregistered seller, the responsibility to pay GST shifts from the supplier (unregistered dealer) to the recipient (registered dealer). The registered dealer is required to generate a self-invoice and pay the GST directly to the government.
For Intra state transactions SGST and CGST are collected while for interstate transactions IGST is collected. However, it’s important to note that not all goods and services fall under this category. Government notifies the cases in which RCM is applicable.
Real estate and construction material purchases are some of the specified goods that fall under this category.
Services Rendered through an e Commerce Operator under Section 9(5) of the CGST Act
RCM is also applicable when certain services are provided through an e-commerce operator and aggregators. In such cases, the e-commerce operator becomes responsible for collecting and remitting the GST to the government on behalf of the supplier.
This majorly applies to the following ecommerce platforms.
- Transportation Services Aggregator: Ola, Uber, Rapido, Porter, etc.
- Accommodation services aggregator: Oyo, MakeMyTrip, Airbnb.
- Housekeeping services aggregator: Urban Company
Registration and ITC under Reverse Charge on GST
Here are some of the important rule to keep in mind when RCM under GST is applicable on a business entity according to Section 24 of the CGST Act, 2017.
-
1. Mandatory Registration: Individuals liable to pay GST under RCM must register under GST, regardless of the threshold limit.
-
2. Mentioning RCM on Invoice: Suppliers of goods must indicate in the tax invoice whether tax is payable under RCM.
-
3. Composition Dealer: Composition dealers must pay tax at normal rates, not composition rates, when discharging RCM liability. They are also ineligible to claim input tax credit on tax paid.
-
4. GST Compensation Cess: GST compensation cess can be applicable to tax payable or paid under RCM.
-
5. ITC for Recipient: Suppliers cannot claim ITC on GST paid under RCM. However, recipients can avail themselves of ITC on GST paid under RCM for goods or services received if they are used or will be used for business purposes.
-
6. ITC Usage: Recipients cannot utilize ITC to offset output GST on goods or services under reverse charge. Cash payment is required for such tax liabilities.
Time of Supply under RCM (with Example)
Time of Supply (ToS) refers to the point in time when a transaction is considered to have occurred for the purpose of determining the applicable tax rate and the liability to pay Goods and Services Tax (GST)under the Reverse Charge Mechanism (RCM). It helps to determine on which month GST should be deposited, Return filing date and claims of ITC. Time of supply is also important while passing RCM entry in Books of account.
Time of Supply for Goods and Services under Reverse Charge Mechanism.
Time of Supply under RCM for Goods
When reverse charge is applicable, the time of supply for goods will be determined based on the earliest of the following dates:
- 1. The date of receipt of goods: This is the date when the recipient physically receives the goods.
- 2. The date immediately after 30 days from the date of issue of an invoice by the supplier: If the supplier has issued an invoice, the time of supply can be 30 days after the invoice date.
- 3. If it is not possible to determine the time of supply using the above methods, the time of supply will be considered as the date of entry in the books of account of the recipient.
| Particulars | Date |
|---|---|
| Date of receipt of goods | 15th September 2023 |
| Issue of Invoice | 1st August 2023 (30 days after Issue of invoice 1st September 2023) |
| Date of entry in the books of account | 25th October 2023 |
| Time of Supply of Goods | 1st September 2023 (30 days after issue of Invoice) |
Time of Supply under RCM for Services
In the case of reverse charge for services, the time of supply will be determined based on the earliest of the following dates:
- 1. The date of payment: This is the date when the recipient makes the payment for the services.
- 2. The date immediately after 60 days from the date of issue of the invoice by the supplier: If the supplier has issued an invoice, the time of supply can be 60 days after the invoice date.
- 3. If it is not possible to determine the time of supply using the above methods, the time of supply will be considered as the date of entry in the books of account of the recipient:
| Time of Supply in Case of Services | Example |
|---|---|
| Date of payment | 10th September 2023 |
| Date of issue of invoice by the supplier | If the invoice is issued on 1st August 2023. (60 days from date of issue of invoice is 1st October) |
| Date of entry in the books of account of the recipient | 20th November 2023 |
| Time of Supply | 10th September |
Accounting of GST under RCM
Accounting of GST under Reverse Charge Mechanism (RCM) involves specific considerations.
- 1. Under RCM, the liability to pay GST is shifted from the supplier to the recipient. Therefore, the journal entry along with GST component will be passed on the books of account of recipient.
- 2. The supplier must issue a tax invoice indicating that tax is payable under RCM in case of goods or services on which RCM applies.
- 3. The recipient needs to prepare a self-invoice for the goods or services received. This self-invoice should include the necessary details such as the recipient’s and supplier’s GSTIN (Goods and Services Tax Identification Number), invoice number, description of goods or services, and applicable tax rates.
- 4. The recipient should record the self-invoiced transaction in their books of accounts on the date of supply.
- 5. The recipient would need to book both inward tax and outward tax on the same entry as the GST paid under RCM would be
- 6. Another entry must be passed on the date on which Tax is deposited.
RCM Accounting Entry under GST (with Example)
The accounting entry for transactions under RCM in GST is different from that of a normal GST entry.
How to Pass a RCM Journal Entry?
In the books of Seller/supplier
The entry on the books of seller or supplier of goods and services would be simple like an unregistered dealer not charging GST.
As
Party A/c Dr
Sales A/c Cr
In the Books of Recipient
In the books of recipient, the entry should book both input tax and output tax. Here is how a typical journal entry under RCM would look like.
RCM Accounting Entry under GST (with Example)
Purchase/ Expense Account Dr.
SGST Input Tax (RCM) Dr
CGST Input Tax (RCM) Dr
(or)
IGST Input Tax (RCM) Dr
To Party/ Creditor A/c Cr
To SGST Output Tax (RCM) Cr
To CGST Output Tax (RCM) Cr
(or)
To IGST Output Tax (RCM) Cr
To TDS (If any) Cr
RCM Entry when GST is Deposited
SGST Output Tax (RCM) Dr
CGST Output Tax (RCM) Dr
To Bank A/c Cr
RCM Journal Entry with Example
Let’s consider a company that purchases services that is under RCM from a vendor for a total invoice amount of ₹10,000. The GST rate applicable is 18%, with 9% for State GST (SGST) and 9% for Central GST (CGST). Since this transaction falls under RCM, the liability to pay GST is on the recipient of the service, which is the company itself. The TDS is charged at 10%.
The accounting entry for Reverse Charge Mechanism in the books of recipient for this transaction would be as follows:
RCM Entry 1
| Debit Accounts | Credit Accounts | Amount |
|---|---|---|
| Purchase/Expense Account | – | ₹10,000.00 |
| SGST Input Tax (RCM) | – | ₹900.00 |
| CGST Input Tax (RCM) | – | ₹900.00 |
| – | Party/Creditor A/c | ₹10,800.00 |
| – | SGST Output Tax (RCM) | ₹900.00 |
| – | CGST Output Tax (RCM | ₹900.00 |
| – | TDS on Services | ₹1,000.00 |
RCM Entry 2
| Debit Accounts | Credit Accounts | Amount |
|---|---|---|
| SGST Output Tax (RCM) | – | ₹900.00 |
| CGST Output Tax (RCM) | – | ₹900.00 |
| – | Bank A/c | ₹1,800.00 |
In a Nutshell
Reverse Charge Mechanism in GST is slightly complex to understand however, in simple words its just shifting the burden of charging and remitting Goods and Service Tax from supplier to receiver.
Here are the key takeaways from the blog.
- RCM is necessary to ensure tax collection even if the supplier is not registered or eligible to pay GST, preventing tax evasion and promoting compliance.
- RCM applies in three major scenarios: specified goods and services, unregistered dealer to a registered dealer, and services rendered through an e-commerce operator.
- The receiver should generate a Self-invoice for every transaction done under the reverse charge mechanism criteria and remit the tax to the government on their own.
- Every business that falls under RCM needs to register for GST, irrespective of the threshold.
- The time of supply of Goods and services under RCM is generally the earliest of receiving of goods or services /Payment, 30-60 days from date of invoice, or date of RCM entry in books of accounts.
- Accounting entry for transactions under reverse charge mechanism (RCM) in recipients’ books must mention both input tax and output tax.
Disclaimer: We publish above information as our best research for updation purpose. We recommend double check the facts from Govt. site before implementation. We will not accept any liability for any loss.
FAQs on Reverse Charge Mechanism in Goods and Services Tax
Q1. What is the RCM rate under GST?
The RCM rate is the same rate at which GST is charged on the goods or services received. You can use the GST rate finder for specific rates and HSN code of goods and services under GST.
Q2. Who is eligible for RCM?
Registered buyers/recipients dealing in goods and services specified by CBIC are mandated to charge RCM. Also, all the ecommerce aggregators should compulsorily charge taxes under GST reverse charge if they fall under the criteria specified under section 9 (5) of CGST Act.
Q3. Why is RCM used in GST?
RCM helps widen the scope of tax levy on various unorganized sectors by shifting the burden of GST payments to the recipient. Additionally, RCM allows for specific classes of suppliers to be exempted from the responsibility of charging GST and enables the taxation of imported services.
Q4. How to calculate RCM?
RCM is calculated based on the applicable GST rates. You can calculate GST on reverse charge mechanism using the same formula as calculating GST. : (Value of Goods/Services) x (Applicable GST Rate). Use HostBooks GST calculator to calculate GST to be charged on RCM.
Q5. What is the limit of RCM on freight?
Currently, there is no threshold limit for RCM on freight. It applies irrespective of the value of the freight.
Q6. Who is exempt from paying RCM?
RCM is not applicable if the supply is exempted, nil-rated, or non-taxable. So a recipient buying exempted, nil-rate and non-taxable supplies is exempt from RCM.
Q7. Is RCM refundable?
Yes, Input Tax Credit (ITC) can be claimed for GST paid under RCM, which can be utilized for future tax liability or claimed as a refund in case of export of supplies
Q8. Is RCM applicable on rent?
Yes, reverse charge is applicable if a business registered under GST rents premises for office or workers from an unregistered landlord.
Q9. How to show RCM in GSTR-1?
RCM transactions should be reported in Table 4B of GSTR-1, which is for outward supplies attracting tax on a reverse charge basis.
Q10. Is the Reverse Charge Mechanism applicable on purchases?
RCM applicability on purchases depends on the goods supplied. If the purchased goods are notified by CBIC, then GST is charged reversely. Please refer to the list of notified goods by CBIC.
Q11. Is RCM applicable to B2C transactions?
Reverse charge under GST transactions depends on various factors such as the type of transactions, GST status of dealers, nature of goods and services supplied, and whether they are notified by the regulatory authorities.

Try HostBooks
SuperApp Today
Create a free account to get access and start
creating something amazing right now!














