A Complete Guide on GST e-Way Bill

What is an e-way bill?
E-way bill or Electronic Way Bill has been rolled out by the Government on February 1, 2018, to facilitate smooth flow of goods within a state and between the states. The e-way bill is generated on the e-way bill portal when the value of goods and exceeds 50,000 INR. In the absence of an e-way bill in case of registered person where the value exceeds 50,000 INR, the movement of goods cannot take place. On the successful generation of the e-way bill, a unique E-way Bill Number (EBN) is issued which is made available to the supplier, recipient, and the transporter.
E-way bill will be applicable to the movement of goods in both inter and intra-state transportation. However, the e-way bill for inter-state movement of goods has been implemented from February 1, 2018. Whereas the rules for intra-state will be rolled out between February 1 to June 1, 2018.
Under which circumstances can e-way bill be generated?
When there is a movement of goods in a vehicle or conveyance of value more than 50,000 INR (either each Invoice or an aggregate of all Invoices) –
- In relation to a ‘supply’
- For reasons other than a ‘supply’ ( For instance, return)
- Due to inward ‘supply’ from an unregistered person
The nature of supply should be:
- Made for a consideration (payment) in the course of business
- Made for a consideration (payment) which may not be in the course of business
- A supply without consideration (without payment) in simpler terms, the term ‘supply’ usually means:
- Sale – sale of goods and payment made
- Transfer – branch transfers for instance
- Barter/Exchange – where the payment is by goods instead of in money
What are the exceptional cases?
In the following cases, the e-way bill needs to be generated mandatorily even if the value of the goods is less than 50,000 INR:
- Inter-State movement of goods by the Principal to the Job-worker
- Inter-State transport of Handicraft goods by a dealer exempted from GST registration
Who is supposed to generate e-way bill?
| Type of Person | Situation | Part | Type of Form |
| Registered Person | Before movement of goods | Part A | Form GST EWB-01 |
| Registered Person who is either the receiver or consignor/consignee | Before movement of goods | Part B | Form GST EWB-01 |
| Registered Person is consignor/consignee and goods are handed over to the transporter | Before movement of goods | Part B | Form GST EWB-01, Part B |
| Transporter | Before movement of goods | Form GST EWB-01, Part A | |
| Unregistered Person | The recipient will be responsible for the compliance | 1. If the goods are transported for a distance of ten kilometers or less, within the same State/Union territory from the place of business of the consignor to the place of business of the transporter for further transportation, the supplier or the transporter may not furnish the details of conveyance in Part B of FORM GST EWB-01.
2. If supply is made by air, ship or railways, then the information in Part A of FORM GST EWB-01 has to be filled in by the consignor or the recipient. |
Things to Remember:
In case of multiple consignments in a single conveyance, form GST EWB-02 should be used to produce a consolidated e-way bill including e-way bill numbers for each consignment.
If both the parties have not created an e-way bill, then the transporter can do so by filling PART A of Form GST EWB-01 on the basis of the invoice/bill of supply/delivery challan.
What are the documents required to generate e-way bill?
- Invoice/ Bill of Supply/Challan related to the consignment of goods
- Transport by road – Transporter ID or Vehicle number
- Transport by rail, air, or ship – Transporter ID, Transport document number, and date on the document
What are the circumstances under which e-way bill is not required?
- Transport of specified goods.
- The mode of transport is a non-motor vehicle
- Goods transported from port, airport, air cargo complex or land customs station to Inland Container Depot (ICD) or Container Freight Station (CFS) for clearance by Customs.
- If the distance between the consigner or consignee and the transporter is less than 10 Kms and transport is intra-state, Part B of e-Way Bill is not required to be filled.
What is the validity of e-way bill?
The period till which the e-way bill is valid depends upon the distance travelled while moving the goods from one place to another. If the distance is less than 100 Kms, the e-way bill is valid for 1 day. And, for every additional 100 Kms or part thereof, the validity is additional 1 day.
What is the process of e-way bill generation?
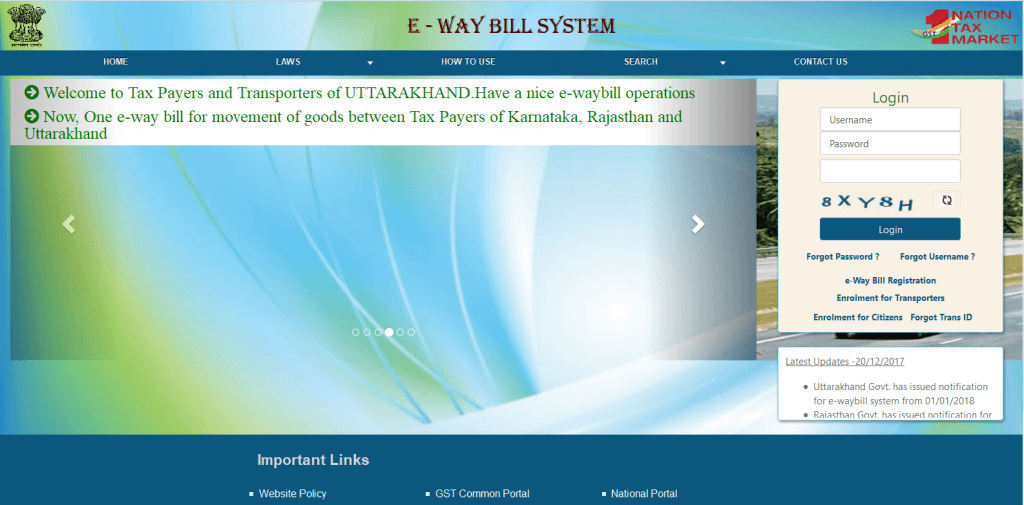
Login
The first step is to login to e-way bill system (ewaybillgst.gov.in). If you haven’t created login yet, you need to generate e-way bill login id and password first. After the login, fill in the details:
Username
Password
Captcha
Next, click on Login.
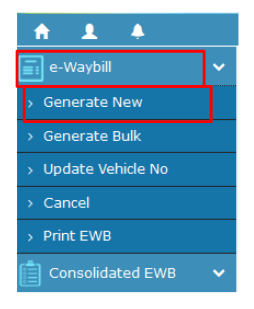
- Generate
The next step is to generate a new e-way bill. Go to the e-way bill section and select “Generate New”. This option is on the left side of the dashboard.
- E-way Bill entry form
After generating a new e-way bill, an entry form will appear on the screen. Now, you need to fill in all the fields of the entry form.
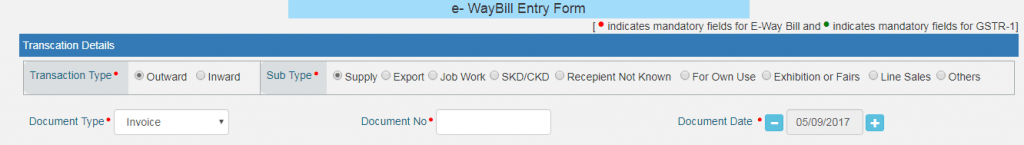
- Transaction Type: Select outward in case of a supplier of consignment and inward in case of a recipient of consignment.
- Sub Type: Select the sub type depending on the type of transaction.
Outward transaction type:
![]()
Inward transaction type:

Here, SKD means Semi Knocked Down and CKD means Complete Knocked Down.
- Document Type: This involves the various types of documents like Invoice, Bill, Challan, Credit Note, and Bill of Entry.
- Document No.: Enter the document/invoice no.
- Document Date: Select the date of the document.
- From/To: This section has to be filled depending on the type of person i.e. supplier or recipient.
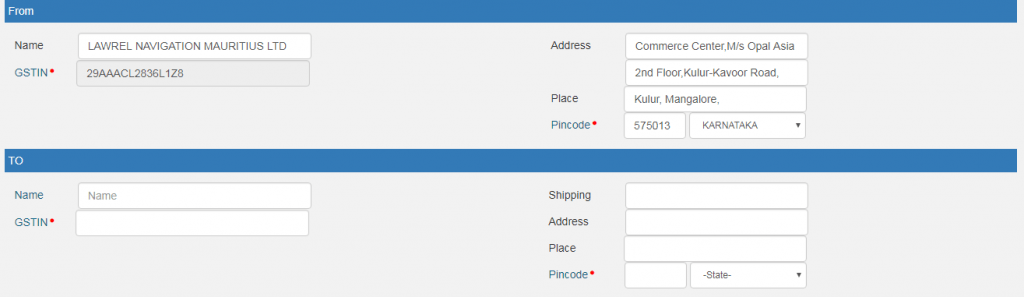
In case of an unregistered person, enter URP in the GSTN field.
- Item Details: Enter the details of the item such as
- Product name
- Description
- HSN Code
- Quantity
- Unit
- Value/Taxable value
- Tax rates of CGST, SGST or IGST (%)
- Tax rates of Cess (%)
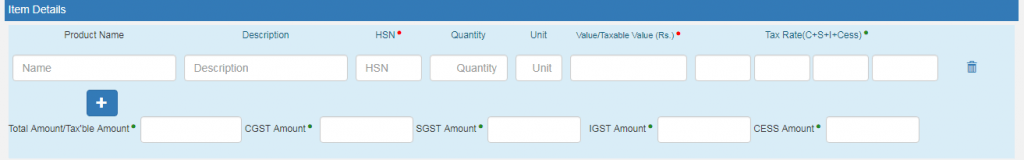
Some entries can be auto-populated in the GST Return while filing a return on the GST portal.
- Transporter Details: This section includes the mode of transport (road/rail/ship/air) and the approximate distance covered (Kms).
In addition, any of the following details should be provided:
Transporter Name/Transporter ID/Transporter Doc No. & Date OR Vehicle No. in which consignment is being transported (Format: AB12AB1234/AB12A1234 /AB121234/ABC1234).
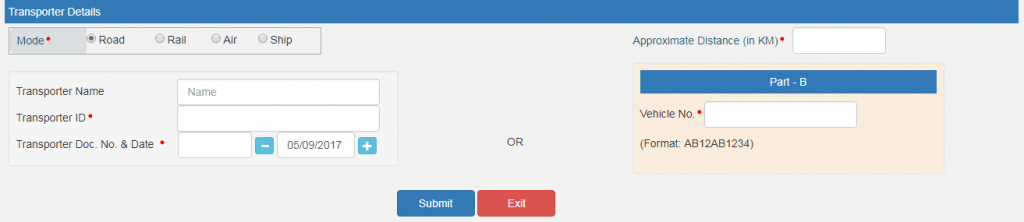
In case of products, clients/customers, suppliers, and transporters used on a regular basis, the ‘My masters’ section on the login dashboard should be updated first.
- Submit
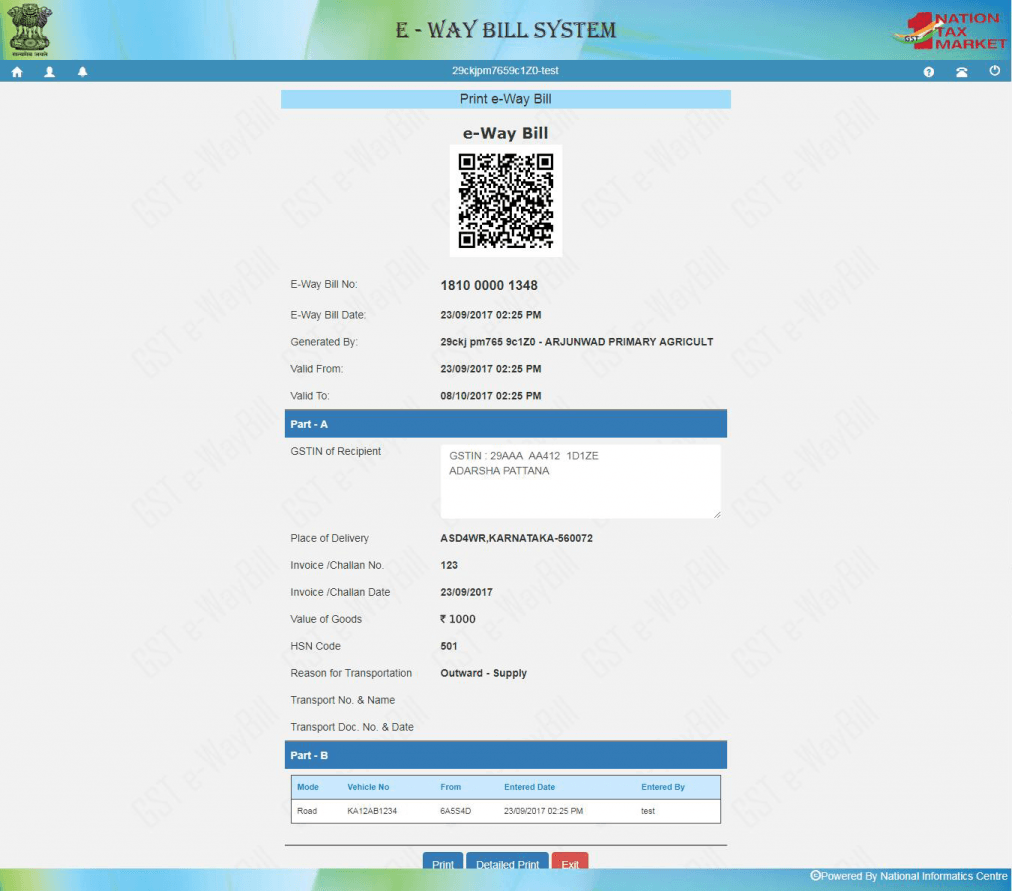
For the submission of the e-way bill, click on “Submit”. The details will be validated and highlighted right away. If there are no errors, the request is processed and the e-way bill in Form EWB-01 will be generated with a 12-digit unique number.
A sample of an e-way bill
- Click on “Print EWB” under e-way bill option.
- Enter the e-way bill number (12 digits) and then click on “Go”.
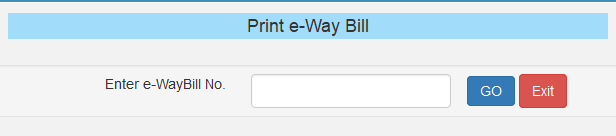
- Click on “Print” or “Detailed Print” that appears on EWB.

After taking the print out of the e-way bill, the concerned person needs to carry the same for transporting the goods.
E-way bill is another initiative taken by the Government to keep a check on the movement of goods between and within the states. Hopefully, the Government will be able to achieve all its e-way bill endeavors.
E-way bill FAQs
- If the validity of the e-way bill expires, what is the course of action to be followed?
Sol. In case the e-way bill expires, then the goods cannot move any further. But, the commissioner of the state can extend the validity as per his discretion. The procedure regarding the same will be notified later.
- If by any chance the invoices get deleted, is there a back-up available in the portal?
Sol. The e-way bill will be available on the GST portal. The same can be checked against the GSTIN of the trader.
- Can e-way bill be generated for a free sample/product?
Sol. Yes, e-way bill can be generated for a free sample/product as well. You just need to enter “Zero” in the quantity and value.
- If two consignments of values 50,000 INR and above 50,000 INR are being transported with the same LR Number, how many e-way bills should be generated in this case?
Sol. It is mandatory to generate an e-way bill for a value exceeding 50,000 INR. However, a person may generate an e-way bill for 50, 000 INR too.
- Should the e-way bill date and invoice date be the same?
Sol. The date on which the e-way bill is generated is known as the e-way bill date. It can differ from the invoice date.
- Is it possible to generate an e-way bill from all the suppliers’ end or can the same be mailed to them in bulk?
Sol. The e-way bill can be generated by the suppliers themselves and the same will also be available on the GST portal which can be accessed through the GSTIN.
- If a person is both a taxpayer and a transporter, how many times should the person get himself registered?
Sol. In this case, a person needs to register as a taxpayer first, log out, then register as a transporter.
- How to generate an e-way bill for import and export transactions?
Sol. Select the Sub-Type ‘Import’ or ‘Export’ & enter the From/To Address of the Supplier/Customer in Other Territory. The Vehicle Number should be updated every time there the vehicle changes til the goods reach the destination.
- What is the process of getting Invoice Reference Number (IRN)?
Sol. A registered person may obtain an Invoice Reference Number from the common portal by uploading, a tax invoice issued by him in FORM GST INV-1 and produce the same for verification by the proper officer in lieu of the tax invoice and such number shall be valid for a period of thirty days from the date of uploading. The registered person will not have to upload the information in Part A of FORM GST EWB-01 for generation of e-way bill and the same shall be auto-populated by the common portal on the basis of the information furnished in FORM GST INV-1.
- Is it possible to re-generated EWB in place of an expired one? What can be the consequences of the same?
Sol. The validity of the EWB number cannot be extended if the validity has already expired. But, you can extend the validity any time before 4 hours of the expiry of the validity period. In such a scenario, we need to extend the validity before the expiry of the same. However, the e-way bill number will be the same.
- Is there an option to update LR (Lorry receipt) number in part B?
Sol. Yes, we can update the LR (Lorry receipt) number in Part B.
- How to generate an e-way bill, if the goods relating to one invoice are being moved in multiple vehicles?
Sol. If the goods are being transported in a Semi Knocked Down (SKI) or Completely Knocked Down (CKI) condition the EWB shall be generated for each vehicle based on the delivery challans issued for that portion of the consignment and
(a) The supplier shall issue the complete invoice before dispatch of the first consignment;
(b) The supplier shall issue a delivery challan for each of the subsequent consignments, along with a reference of the invoice;
(c) Each consignment shall be accompanied by copies of the corresponding delivery challan along with a duly certified copy of the invoice; and
(d) The original copy of the invoice shall be sent along with the last consignment. The EWB has to be generated for each consignment based on the delivery challan details along with the corresponding vehicle number.
- In the section “Outward Supply”, what are “CKD/SKD” & “Line sales”?
Sol. “CKD/SKD” means the movement of the goods in Completely Knocked Down condition or Semi Knocked Down condition. For instance: Movement of different parts of an object, which will be assembled later.
“Line Sales” Vertical sales made from one unit /department/division of an organization to another unit/department/division next in production line within that organization
- Should an e-way bill be generated for the movement of goods from one unit of the company to another through owned vehicle located within 10 kms?
Sol. Yes, e-way bill is required to be generated even in case of movement of goods within 10 kms. The relaxation updating part B (vehicle details) is given only in cases of movement of goods from the place of business of consignor to the business of transporter for further movement of such goods. Hence, in all other cases, e-way bill needs to be generated even if the distance to be covered is less than 10 kms. In case the motorized vehicle is not used for transportation of vehicle, E-way bill is not required.
- Is an e-way bill required against cancelled invoices or a credit note?
Sol. In this case, the transporter can generate an e-way bill with the help of supplier or recipient by indicating supply as ‘Sales Return’ and with relevant document details. The goods can be returned to the supplier as per the agreement. E-way bill will be generated against the Credit Note.
- How will Customer predict the number of Delivery Challans that should be generated in case the transporter divides the big truckload into smaller tempos?
Sol. If some of the goods are transferred to another vehicle, then delivery challans should be generated in respect of the goods loaded in other vehicles.
- How to generate EWB if the Billing Address & Shipping Address are different?
Sol. In case of bill to and ship to, the transporter would be at the supplier’s location and can personally collect the invoice and e-way bill from the supplier. As far as invoice and e-way bill of the buyer in the name of consignee (ship to party) is concerned it should be handed over to the transporter. The buyer may also obtain an Invoice Reference Number (IRN) from the common portal in Form GST INV-1 and convey the same with the E-way bill number to the transporter.
- In case “Bill To” & “Ship To” party are different, how is one supposed to measure the distance in part A? If A is the sender, B is the “Bill To” party & C is the “Ship To” party, should e-way bill be generated for A to B & B to C or directly A to C?
Sol. If the addresses involved in ‘Bill to’ and ‘Ship to’ in an invoice/bill belong to different taxpayers, then two e-way bills will be generated. One e-way bill for the first invoice and the second e-way bill is from ‘Bill to’ party to ‘Ship to’ party based on the invoice/bill of the ‘Bill to’ party. This completes the cycle of transactions and the taxes will change for inter-state transactions. The distance will be measured as per the address mentioned in the e-way bill.
- If the e-way bill is generated by some other party against the taxpayer’s GSTIN, how would the taxpayer or recipient come to know about the same?
Sol. As per rules, the taxpayer or recipient has an option to reject the e-way bill generated on his GSTIN by other parties. The following options would enable him to keep a track of e-way bills generated against his GSTIN.
- He can view it on the dashboard, once he logs into the system.
- He will be informed through an SMS, the e-way bill activities on his GSTIN.
- He can go to the reject option and select the date and see the e-way bills. Here, the system shows the list of e-way bills generated on his GSTIN by others.
- He can go to report section and see the ‘EWBs by other parties.
- How is an E-Way Bill generated in case of Out to Out Shipments?
Sol. If the addresses involved in ‘Bill to’ and ‘Ship to’ in an invoice/bill belongs to one legal name/taxpayer as per GSTIN within the state, then one e-way bill has to be generated. If the ‘Bill to’ is the principal place of business and ‘Ship to’ is an additional place of business of the GSTIN or vice versa in an invoice/bill, then one e-way bill is sufficient for the movement of goods. But, if the addresses involved in ‘Bill to’ and ‘Ship to’ in an invoice/bill belongs to different legal names/taxpayers, then two e-way bills have to be generated. One e-way bill for the first invoice, the second e-way bill is from ‘Bill to’ party to ‘Ship to’ party based on the invoice/bill of the ‘Bill to’ party. This completes the cycle of transactions and taxes will change accordingly for inter-state transactions.
E-way bill is another initiative taken by the Government to keep a check on the movement of goods between and within the states. Hopefully, the Government will be able to achieve all its e-way bill endeavors.

Try HostBooks
SuperApp Today
Create a free account to get access and start
creating something amazing right now!















7 Comments
Well written and well explained too. Eagerly waiting for HostBooks to launch e-way bill section of GST. Please let me know by when can that be expected.
good and service tax is very vast. And detailed information provided by you is very helpful for me
Well written on e way bill
I absolutely love your blog and find many of your post’s to be what precisely I’m looking for. can you offer guest writers to write content for you personally? I wouldn’t mind creating a post or elaborating on many of the subjects you write related to here. Again, awesome blog!
That’s nicely explained..
I am so happy to ready this. This is the kind of manual that needs to be given and not the random misinformation that is at others blog.
I appreciate your sharing this best article.
Thanks a lot for sharing this blog post. It helped me understand e-way bill more clearly and I was able to generate my e-way bill correctly.